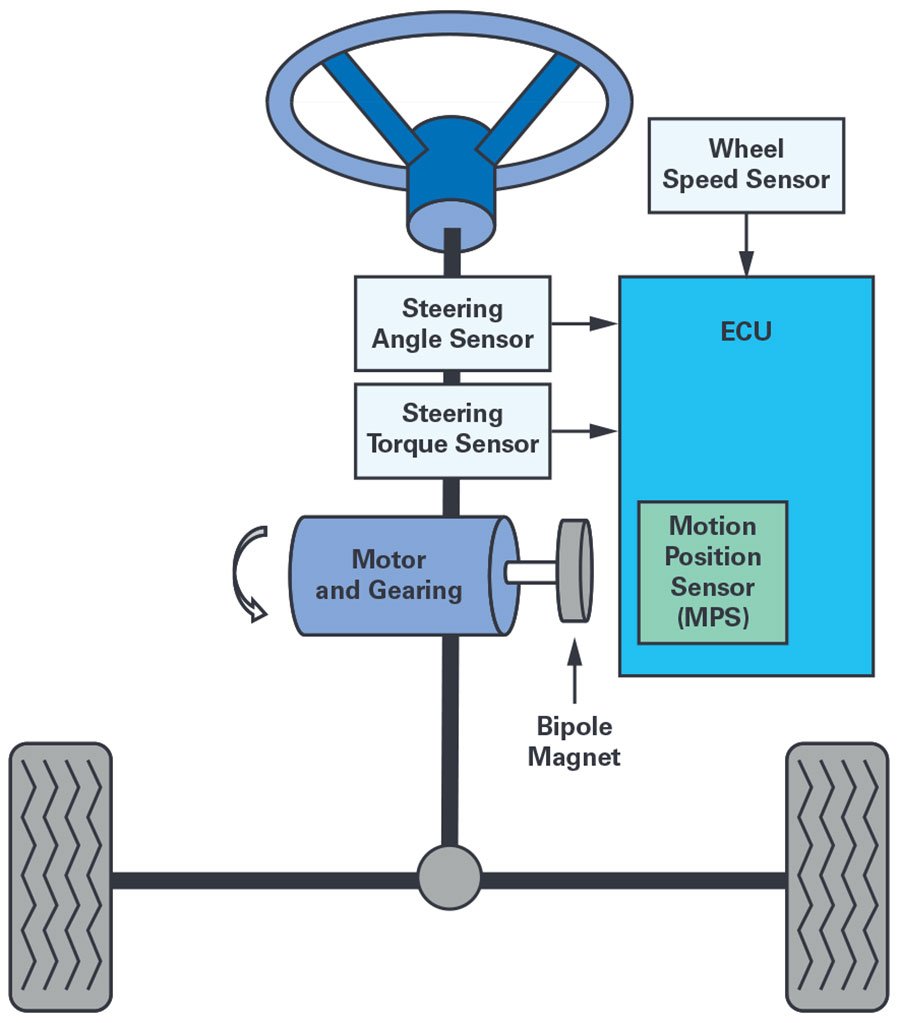
Power steering systems play a crucial role in modern automobiles, making it easier for drivers to control their vehicles and navigate through various road conditions. Two common types of power steering systems are electric power steering (EPS) and hydraulic power steering (HPS). In this article, we will explore the differences between EPS and HPS technologies, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Electric Power Steering (EPS):
Electric power steering, often referred to as EPS, has gained popularity in recent years due to its efficiency, reduced complexity, and environmental friendliness. EPS systems replace the traditional hydraulic setup with an electric motor that assists the driver in turning the wheels. Here are some key features of EPS:
- Efficiency: One of the primary advantages of EPS is its efficiency. Since it operates on an as-needed basis, the electric motor only consumes power when the driver applies force to the steering wheel. This results in fuel savings compared to hydraulic systems, which constantly draw power from the engine.
- Compact Design: EPS systems are relatively compact, as they eliminate the need for hydraulic fluid, pump, and associated components. This not only reduces weight but also frees up space under the hood.
- Variable Assist: EPS systems can provide variable levels of assistance, making it easier to adapt to different driving conditions. For example, at higher speeds, the system may reduce assistance to enhance stability; at lower speeds, it can offer more assistance for ease of parking. it is also useful for advanced driver assistance features like adaptive cruise control, lane keep and more.
- Environmental Benefits: EPS is considered more environmentally friendly because it eliminates the need for hydraulic fluid and reduces the risk of fluid leaks, which can harm the environment. Additionally, it consumes less energy, contributing to lower emissions.
Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS):
Hydraulic power steering, or HPS, has been a staple in the automotive industry for many years. It uses hydraulic fluid, a pump, and a series of hoses to provide steering assistance. Here are some key features of HPS:
- Proven Technology: HPS has been in use for decades and is a proven and reliable technology. Many drivers appreciate its consistent and predictable steering feel.
- Responsive Feedback: HPS systems are known for providing direct and responsive feedback to the driver, offering a more connected driving experience.
- Lower Initial Cost: Traditionally, HPS systems have been more affordable to manufacture and install, which can result in lower initial vehicle costs.
- Simple Maintenance: Maintaining HPS systems is relatively straightforward, and repairs are generally easier to conduct compared to EPS systems.
Comparing EPS and HPS:
- Fuel Efficiency: EPS is more fuel-efficient than HPS since it only draws power when needed, reducing the load on the engine. This can lead to improved gas mileage.
- Steering Feel: While HPS is praised for its responsive feedback, EPS can be programmed to mimic different steering “feels,” allowing manufacturers to tailor the driving experience to suit their target audience.
- Environmental Impact: EPS is considered more environmentally friendly due to its reduced energy consumption and the elimination of hydraulic fluid.
- Maintenance and Repairs: HPS systems are generally easier and less expensive to maintain and repair. In contrast, EPS systems can be more complex to service.
- Cost: Initially, HPS systems have been cheaper to implement, but as technology advances, the cost difference between the two has decreased.
Conclusion:
The choice between electric power steering (EPS) and hydraulic power steering (HPS) ultimately depends on a variety of factors, including the vehicle’s intended use, the desired driving experience, and environmental concerns. While EPS offers better fuel efficiency and adaptability, HPS is known for its reliable and direct steering feedback. As technology continues to advance, EPS systems are becoming more prevalent, but HPS still has its place in the automotive world, especially in certain applications, such as when driving sports cars, where the traditional feel of hydraulic assistance is valued.