We all drive cars in our lives, but most of us do not know or understand what is our cars drivetrain. There are different types of drivetrains. To be precious there are 4 types of drivetrains in vehicles, All Wheel Drive (AWD), Front Wheel Drive (FWD), Rear Wheel Drive (RWD), Four Wheel Drive (4WD). We will explain each of the drivetrain in detail, with its pros and cons. First, let us understand what is a drivetrain in a car. The drivetrain is the system that connects the transmission to the drive axle. It transfers the power generated by the engine to the wheels.
How many drivetrains are there?
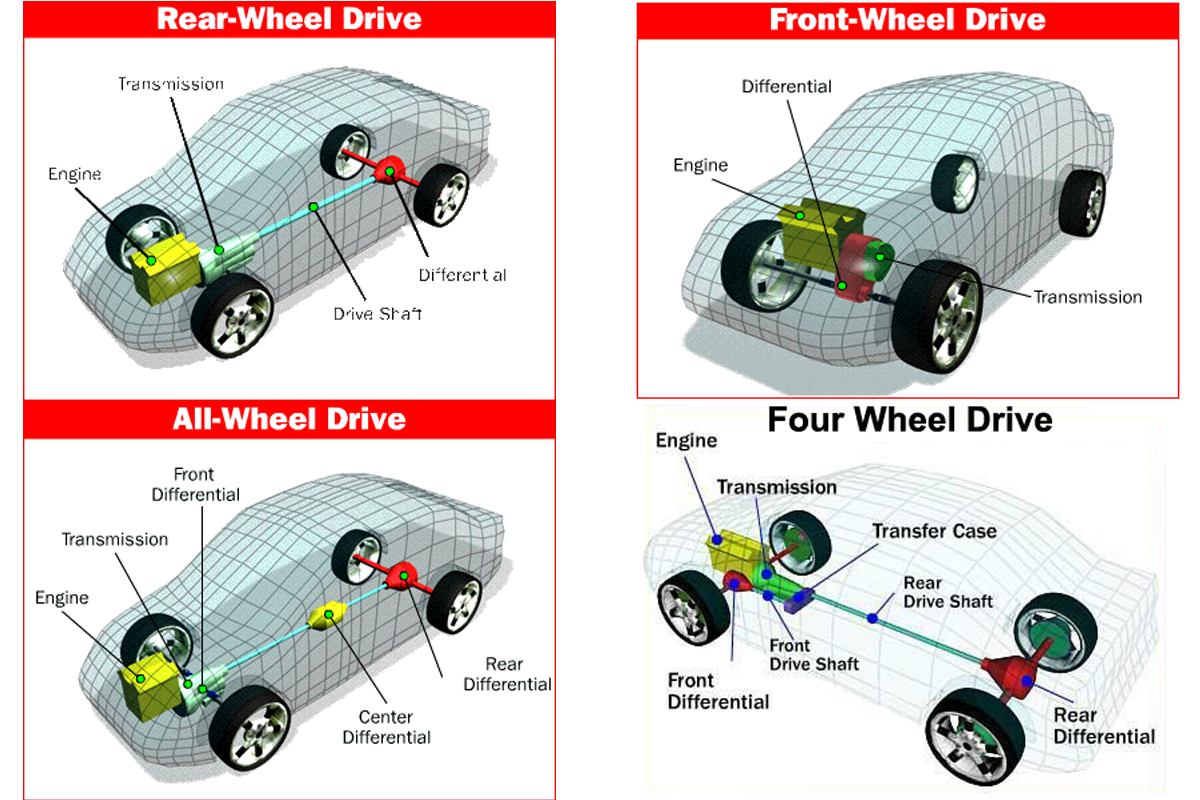
There are 4 different types of Drivetrains, FWD, RWD, AWD, and 4WD. Now let’s dive into 4 different types of drivetrains in vehicles.
AWD (All Wheel Drive)

It is mostly used in regular cars, not for deadly offloading but to have traction on the surface like snow, sand or water on the road. AWD is not always on, by default it drives like normal RWD or FWD unless there is a wheel slip. It is mostly an automatic system, where the ECU (Electronic Control Unit) of the car detects which wheel is losing traction activates the AWD and sends the 50% of required power to the wheels losing grip automatically.
This AWD is mostly used in sports cars like Nissan GT-R r35 and Audi R8, this system helps the car to have a good launch and also helps it in the corners has better handling, and utilizes complete power from the engine.
AWD is expensive cause it has a complex hardware system, and the fuel efficiency of the car is also low when it is on AWD. The fuel efficiency is improved because modern-day cars are not always AWD, they are RWD or FWD and switch to AWD when needed.
Advantages:
- It provides increased grip and control under all road conditions.
- Gives sportier handling and traction to a broader range of cars.
- Works all the time (Mostly the computer decides according to the condition)
Disadvantages:
- Reduces Fuel Economy
- Increases the weight and complexity of vehicles
- Not as good in extreme off-road conditions
Courtesy CNET youtube channel
4wd (Four Wheel Drive)
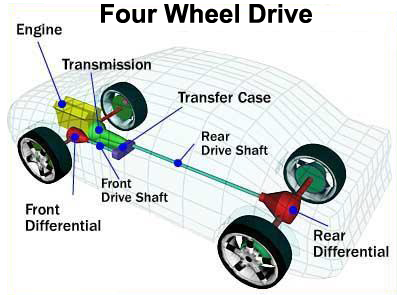
4WD is mostly used for heavy off-roading. The power from the engine goes through the transfer case. This transfer case splits the power between the front and the rear axle so that the torque is evenly split. Then those axles sent the torque to the individual wheels. The transfer case splits power evenly ensuring that all four-wheel spin at the same speed, but this is not possible when the car is turning cause the inside wheel has to turn more slowly than the outside wheel, which covers more ground.
To solve this problem part-time 4WD is introduced which runs on two wheels in normal conditions and when the traction is less you can activate the 4WD via protruding lever or electronically when you require power on all four wheels. In 2WD the car has fewer restrictions on front wheels motion, and you also get better fuel economy in 2WD than 4WD.
There are 2 gears in 4WD ‘High’ and ‘Low’. High gear limits available power to the wheels so you can move quickly over slippery surfaces. The Low gear limits wheel speed but is perfect for difficult terrain. High gear has a limit of up to about 55 mph, but in Low gear, you cannot go fast if you do it might cause damage.
Advantages:
- Best traction in off-road conditions.
- It can be turned off to improve fuel economy.
- Proven, rugged technology.
Disadvantages:
- Adds weight and complexity to cars.
- It can’t be used in all conditions.
- More expensive than two-wheel-drive models.
- Not suitable for on-road conditions
FWD (Front Wheel Drive)

FWD (Front Wheel Drive) is nowadays common in daily driven cars because of its stability and efficiency. It has less weight which means better fuel economy. The engine is mounted either sideways or longitudinally which puts weight on the front wheels, because of this there is better traction while driving. The transmission and differential are connected with one unit called a transaxle. Complex universal joints connect the wheels to the axle, allowing a smooth transmission of power while the wheels turn, causing the front wheels to be responsible for steering, wear on tyres and suspension happens more quickly.
There is no driveshaft going from the front of the car to the back cause the powertrain is a single unit in the engine compartment, this increases interior space as there is no space occupied by the rear differential.
Advantages:
- Low weight, because all the components are in front and one additional differential and driveshaft which transfers the power to the rear axle is removed.
- Low cost.
- Better Fuel Economy.
- Better traction on a slippery surface (snow).
Disadvantages:
- The centre of gravity of the vehicle is typically farther forward than a comparable rear-wheel-drive layout.
- Chances of understeering at a high-speed cornering.
- In low traction conditions, the front wheel will lose traction making steering ineffective.
RWD (Rear Wheel Drive)
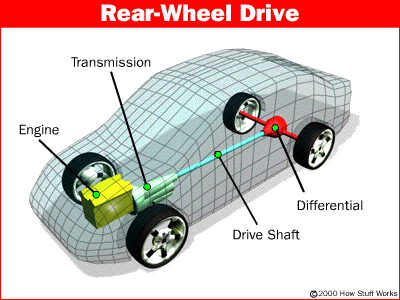
It is the oldest drivetrain used in cars, today most cars have RWD cause it provides better handling on dry surfaces. RWD systems use a long driveshaft that transmits power from the engine in the front of the vehicle to the differential at the rear axle. The driveshaft is connected to transmission and differential via universal joints which helps the driveshaft rotate easily. The rotation motion of the driveshaft rotates the differential and the differential rotates the wheels.
In the case of Rear engine and rear-wheel drive or mid-engine rear-wheel drive a transaxle is used just like FWD (Front-wheel Drive) vehicles because you dont need a driveshaft to send the power to the rear wheels.
Advantages:
- Better handling in dry conditions, because the rear wheels will have more grip on a dry surface.
- Better Weight distribution.
- The work is distributed to both front and rear axles. Front axle steering and braking and Rear axle powering the car.
Disadvantages:
- Oversteer
- The overall weight of the car is increased because the components are increased.
- Handling can be tricky if the driver is new.
- Also in the front engine RWD car, traction on slippery conditions is bad.
Conclusion
Hope you get an idea about different types of drivetrains in vehicles. You can know what is your vehicle’s drivetrain by just searching your car’s name and drivetrain, you will know your vehicle’s drivetrain.
So in my opinion, if you are a rookie driver FWD is best and reliable and fuel-efficient. RWD is good for experienced drivers as it tends to sideway if you accelerate harder. And if you looking for racing AWD is best as it has the most grip and it can get you off the line more quickly. 4WD is strictly for offloading only and can not be used in day-to-day life.



One Reply to “What are the different types of Drivetrains? AWD vs FWD vs RWD vs 4WD”