As AI/ML deployments move from prototypes to production, annotation pipelines must support both volume and precision under real-world conditions. This blog focuses on designing a human-in-the-loop annotation approach that enhances efficiency without compromising accuracy, using AI-assisted pre-labelling, defined review workflows, and continuous feedback into model refinement. It also highlights operational practices, quality assurance, confidence scoring, and drift monitoring, that keep annotation outputs aligned with evolving data and business requirements. Let’s explore further!
How Does Human-in-the-Loop Annotation Accelerate AI/ML Development?
1 Enhanced Annotation Quality
Automated labelling accelerates throughput but can introduce systematic errors, particularly under ambiguity or domain-specific semantics. Human oversight increases label fidelity, reduces label noise, and prevents error propagation into training data, directly improving downstream model performance.
Example: In computer vision tasks such as object detection, automated labels can degrade under occlusion, low illumination, motion blur, or non-standard viewpoints. Manual annotators validate and correct these cases to maintain consistent training signal quality.
2 Resolved Ambiguous Edge Cases
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) annotation addresses complex edge cases by integrating domain expertise into AI/ML development workflows where automated systems encounter ambiguity, rare scenarios, or limited context. Manual annotators provide contextual interpretation for subtle variations, such as partially occluded objects in computer vision or atypical patterns in medical imaging, where pattern-based automation can be unreliable.
In domain-sensitive use cases, subject-matter experts validate machine-labelled outputs to ensure low-frequency, high-impact events are annotated accurately and aligned with operational, safety, and regulatory expectations. This reduces critical mislabels in training data and improves downstream model reliability.
3 Model Refinement Through Iterative Feedback
Human-in-the-loop workflows support continuous model improvement through structured feedback cycles between AI-assisted data abeling and manual review. Corrections and reviewer decisions are captured as high-quality training signals, enabling the model to progressively reduce recurring error patterns and improve performance on newly observed data. Over time, this increases pre-label accuracy, reduces manual effort per batch, and stabilizes label consistency. When paired with active learning, the workflow prioritizes high-uncertainty samples for human review, improving sample efficiency and accelerating model convergence.
4 Addressing Data Imbalances
Data imbalances, where certain categories of data are underrepresented, are a common problem in many machine learning tasks. Human-in-the-loop annotation appraoch can help address this issue by enabling humans to prioritize annotating underrepresented classes. For instance, in medical imaging, rare conditions may only appear in a small percentage of images, but their accurate labelling is crucial for model performance.
5 Scalable Annotation Pipelines
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) annotation enables scalability through AI-assisted pre-labelling and confidence-based routing. HITL provides flexibility through a modular pipeline (pre-labelling, manual validation, QA) that supports rapid updates to label schemas, guidelines, and review depth without interrupting throughput. In practice, capacity can be managed through skill-tiered resourcing (general annotators and domain SMEs) and clear escalation paths, allowing teams to balance volume and quality. This applies across modalities, image annotation (bounding boxes, segmentation), video annotation (object tracking across frames), and text annotation (classification, entity tagging).
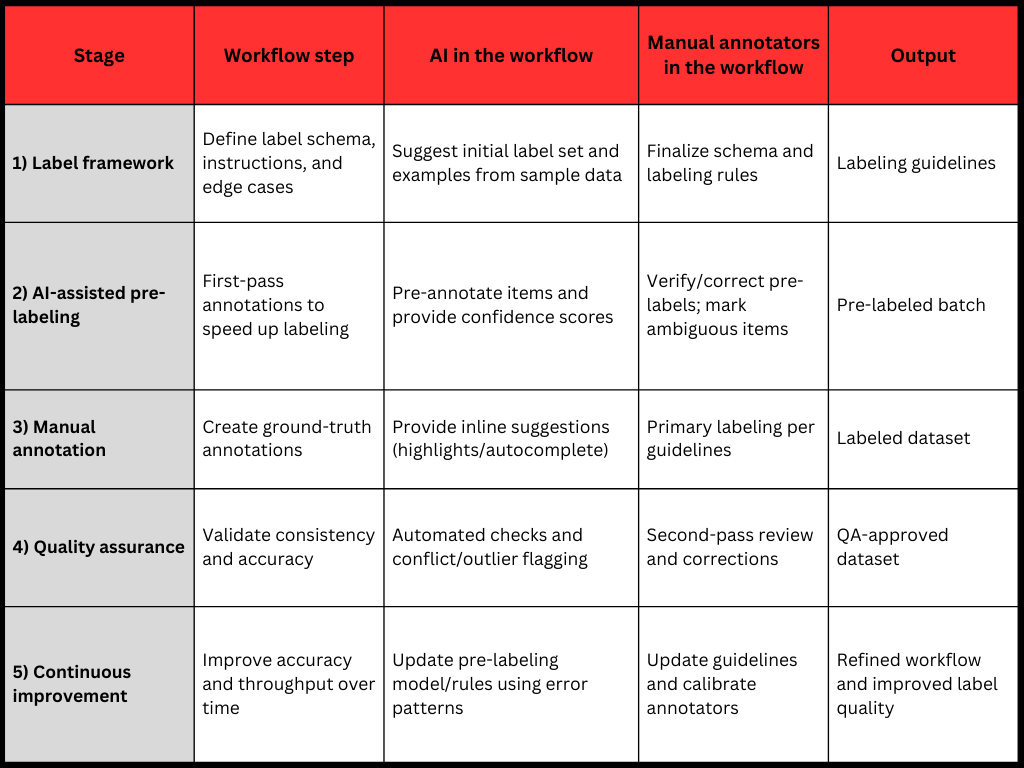
Best Practices for Human-in-the-Loop Annotation
1 Develop Clear and Detailed Annotation Guidelines
Implementing thorough and well-defined annotation guidelines is essential for ensuring consistency across both automated and human-powered annotation tasks. These guidelines minimize ambiguity, reduce variability, and establish uniform standards, thereby enabling accurate and reliable labelling throughout the entire workflow.
2 Deploy a Robust Quality Assurance Framework
A comprehensive QA framework is vital for maintaining accuracy at scale. This framework should incorporate processes like inter-annotator agreement evaluations, traceable documentation, and performance benchmarks to ensure that annotation quality is consistent and dependable across large datasets.
3 Leverage Confidence-Scoring in Annotation Workflow
By incorporating confidence scores, automated systems can prioritize high-certainty predictions for machine processing while directing uncertain or complex tasks to human annotators. This approach ensures that human resources are allocated efficiently, focusing on more challenging data points while optimizing overall workflow productivity.
- Tier 1: High-Confidence Tasks (AI-Assisted): AI/ML models pre-annotate data with high confidence, particularly for straightforward tasks, such as clear images or simple text classifications. Human reviewers quickly verify these annotations, significantly reducing time spent compared to full manual labelling.
- Tier 2: Moderate-Confidence Tasks (Standard Annotators): Data with moderate AI confidence or uncertainty is routed to standard annotators. These tasks may undergo double annotation by multiple reviewers, with an adjudication process to resolve discrepancies and ensure accuracy.
- Tier 3: Low-Confidence & Edge Cases (Experts/SMEs): For cases with low AI confidence or ambiguous data, subject matter experts (SMEs) are engaged to provide specialised knowledge and accurate data labelling workflows. This ensures that complex or critical cases are handled with the required expertise.
4 Integrate Continuous Feedback into Model Improvement
To drive continuous model enhancement, human corrections should be seamlessly integrated into the retraining process. This feedback loop enables the automated system to learn from verified annotations, minimizing recurring errors, improving accuracy, and ensuring that each annotation cycle builds on the previous one.
5 Regularly Monitor for Data Drift and Adapt Models
Consistent monitoring of data patterns and model performance is critical for detecting data drift. Proactively updating models in response to these shifts ensures that the annotation outputs remain relevant and accurate, effectively aligning with changes in real-world data conditions over time.
In-house annotation teams often lack the infrastructure for throughput scaling, operational standardization, and access to domain SMEs, which can drive longer iteration cycles and higher annotation overhead. Outsourcing data annotation services addresses these gaps through established data labelling workflows, multi-stage review and QA frameworks, AI-assisted pre-labelling with confidence scoring, and domain expertise for complex cases


