Hello, guys today I will tell you how the braking system works in cars and the types of brakes available for cars.
What are Brakes?
Brakes are one of the most important components of a vehicle. If you talk about performance it includes good brakes also, because if you go fast you need the same amount of stopping power to reduce that speed.
It is a mechanical device that absorbs energy from a moving system. It is used to slow or stop a moving vehicle, which is mostly accomplished by means of friction.
In modern cars, we have ABS (Anti-lock braking system), which prevents you from locking your wheels and losing control of the steering. How does the ABS braking system works? In a small amount of time, ABS will release its brakes multiple times in many repetitions. Since this braking system uses computer-aided software to control the pumping, the driver has to apply pressure on the brake pedal continuously so that the ABS comes into action and brings back the vehicle in a controlled steering state in cases where it might skid.
How Braking system works?
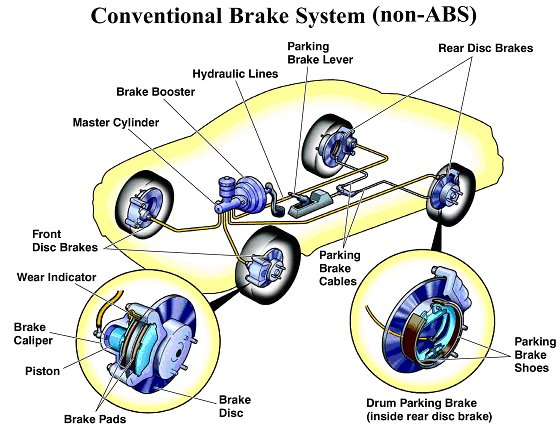
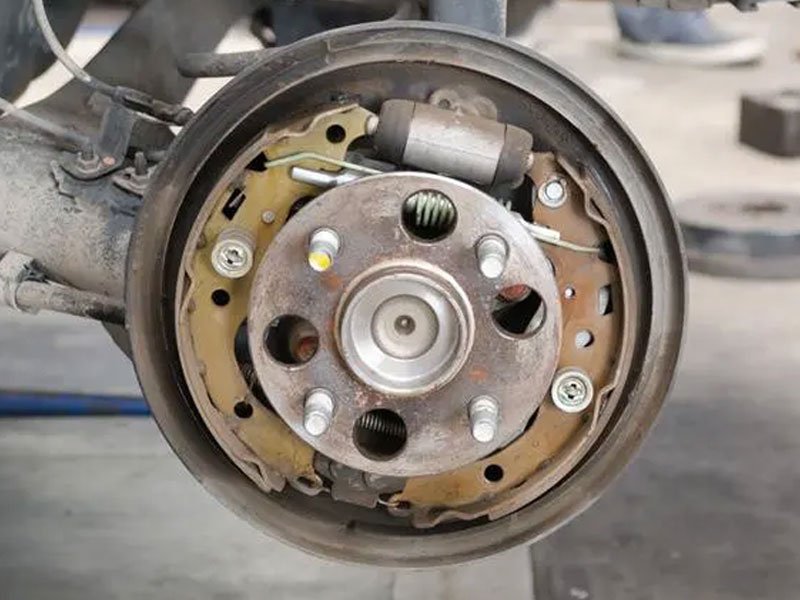
There are two kinds of brakes Disc Brakes and Drums Brakes. Disc brakes are mounted on the front wheels and Drum brakes are mounted on the rear wheels. Some modern high-end cars have a Disc brake on all four wheels.
These are the components used in the brake system:
Brake Pedal:
It is located in the centre of the accelrator and clutch pedal in manual transmission vehicles, and in automatic transmission, the pedal on the left is the brake pedal. The brake system is activated only after pressing this pedal.

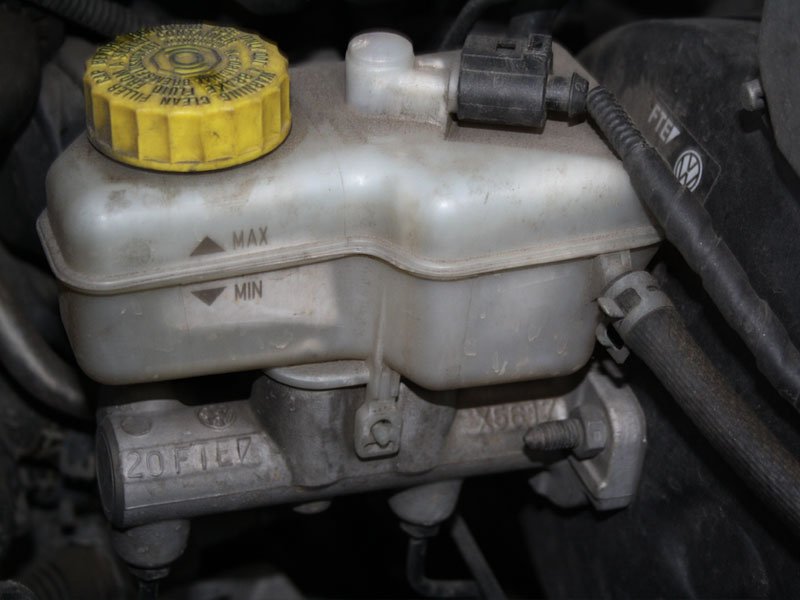
Fluid Reservoir
It is the brake fluid or brake oil that is used on the braking system.

Fluid Lines
These are pipes through which the brake fluid flows in the vehicle.
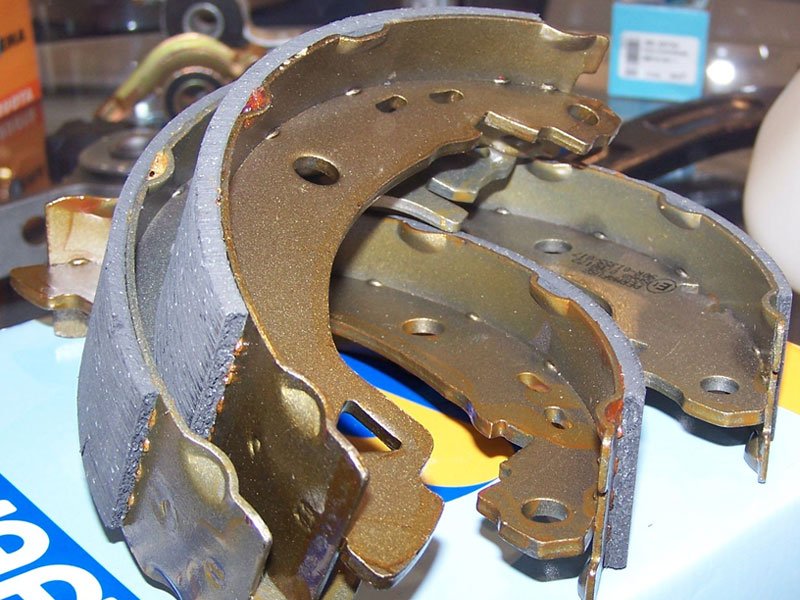
Brake Pads
Steel backing plates are used in disk brakes. It is usually made of ceramic, metal or other hard-wearing composite materials.

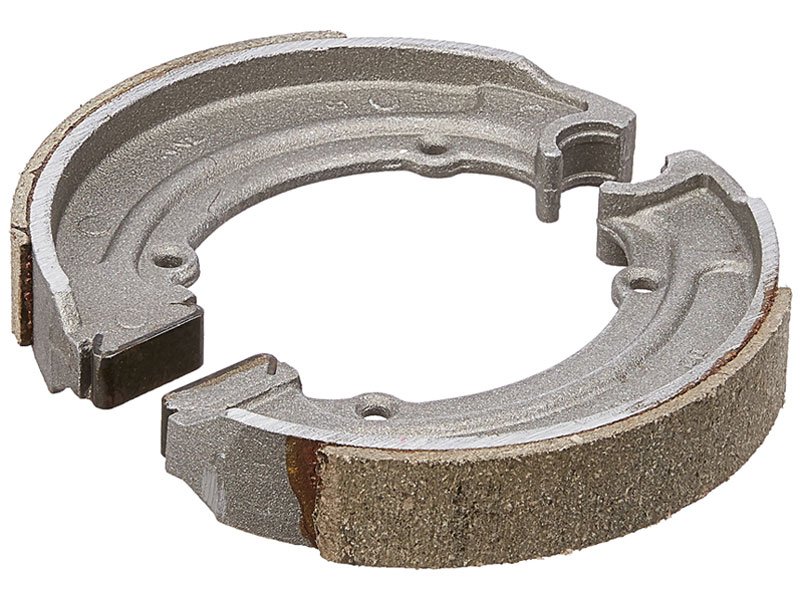
Brake Shoes
2 pieces of sheet steel welded together that carry the brake lining.

Brake Drum
It is the rotating drum-shaped component used in drum brakes.

Brake Rotor/Disc
It is a cast-iron brake disc connected to the wheel and/or axle, sometimes made of reinforced carbon, ceramic matrix or other composites.

Brake Lining
It is a heat-resistant, soft but tough material with a high friction characteristic housed inside a brake shoe.

Brake Piston
It is a moving component contained by a cylinder. There can be 1,2,4,6,8 piston, but typically you will find 4 or 6-piston callipers in modern cars

Brake Calliper
A device on which brake pads and pistons are mounted
Floating Calipers/Sliding Caliper: It moves relative to the rotor; and uses a piston on a single side of the disc to push the inner brake pad into the braking surface before pulling the calliper body in to apply pressure on the opposite side of the disc.
Fixed Calipers: It does not move relative to the rotor and is sensitive to imperfections; it uses one or more single pairs of opposing pistons to clamp from each side of the rotor.

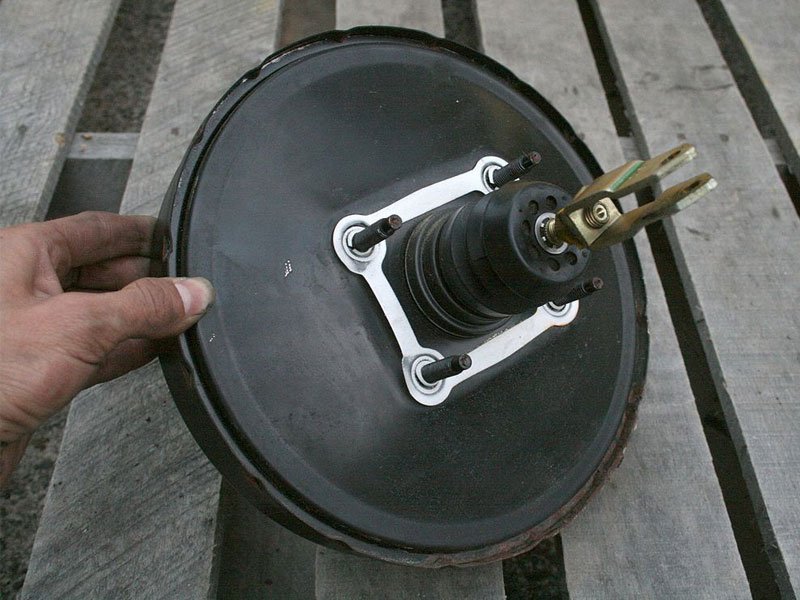
Master Cylinder
A device that converts the non-hydraulic pressure from your foot into hydraulic pressure and controls slave cylinders at the opposite end of the hydraulic system.

Vacuum Booster
A component used to enhance the master cylinder and augment pressure from a driver’s foot through the use of a vacuum in the engine intake; is only effective while the vehicle’s engine is running.
When the driver presses the brake pedal there is a force generated which is boosted by the Vacuum from the engine. This boosting effect causes the brakes to respond more quickly.
This force from the vacuum booster pushes the piston inside the master cylinder against the spring force causing the brake fluid to flow under pressure. This pressurized fluid reaches the brake calliper (Disc Brakes) and brake cylinder (Drum Brakes) via fluid lines.

There are 2 types of brakes
Disc Brakes
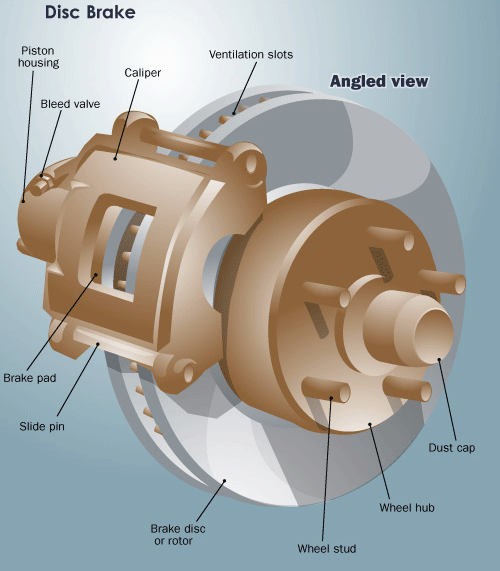
The pressurized fluid enters the brake calliper forcing the brake pads to move inwards against the revolving disc (which is connected to the front wheels). When the brake pads come in contact with the disc, friction is generated which reduces the speed of the disc which in turn reduces the speed of the vehicle and eventually stopping your vehicle.
Drum Brakes
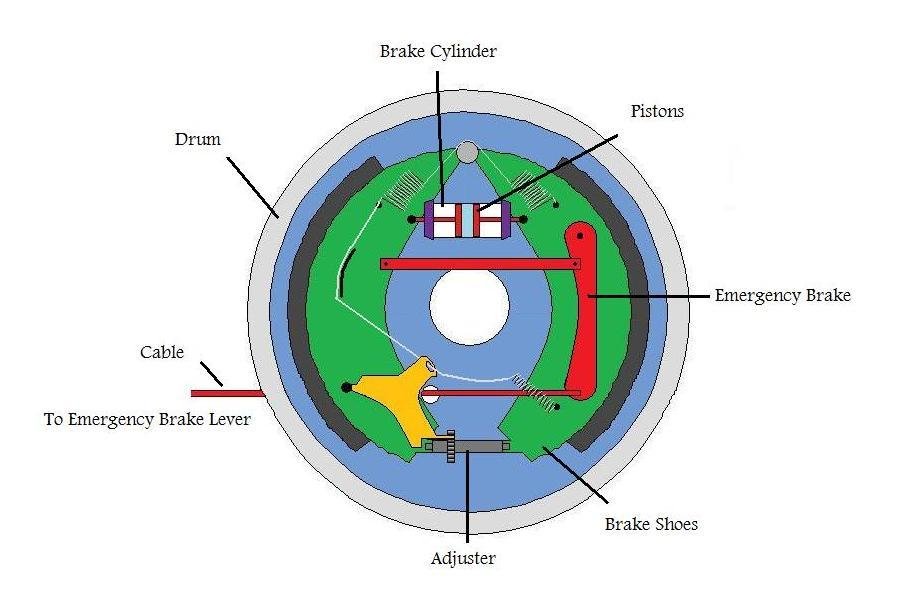
The pressurized fluid now enters the brake cylinder inside the Drum brakes. There is a piston inside these cylinders, these pistons move outwards because of the brake-pressurized fluid inside the cylinder. This outward movement of the piston causes the brake shoes to move towards the rotating drum. When these brake shoes rub against the drum, friction is generated converting the kinetic energy into heat energy and thereby stopping your vehicle.
Courtesy: Automotive Basics
Types of Brakes system
Electromagnetic Brake System
Electromagnetic brakes are becoming popular nowadays. It uses an electric motor that is included in the automobile which helps the vehicle come to a stop. It is mostly found in hybrid and electric cars and uses an electric motor to charge the batteries and regenerative brakes.
Frictional Brake System
It is the traditional braking system and is commonly found in most automobiles. They are service brakes, and typically found in two forms; Pads(Disc) and Shoes(Drums). As the name implies, these brakes use friction to stop the automobile from moving. The pads are located on top of the disc which is rotating with the front wheel, and the shoes are located inside the drum which is rotating with the rear wheel. The pads will close in on the disc and stop the vehicle and the shoes will expand and rub with the drum to stop the vehicle.
Hydraulic Brake System
A hydraulic brake system is composed of a master cylinder that is fed by a reservoir of hydraulic braking fluid. This is connected by an assortment of metal pipes and rubber fittings which are attached to the cylinders of the wheels. The wheels contain two opposite pistons which are located on the band or drum brakes which pressure to push the pistons apart forcing the brake pads into the cylinders, thus causing the wheel to stop moving.
Hopefully, you now understand what are brakes and their types and how the braking system works. If you have any questions please let me know in the comments.


One Reply to “What are brakes & How Braking system works in Cars”