When starting your own business, you have a ton of important decisions to make. However, probably the most important one, the one you have to make very early on in your brand formation, is selecting which type of business organization. This decision is so crucial that it will influence the structure, taxation, liability, and management of your company. Of course, each different business structure offers a different set of pros and cons, so it’s essential to understand all the benefits and drawbacks of each system before you settle on one that fits your needs. The systems differ on legal requirements, expenses, and paperwork, so it’s important to examine your business goals, the structure of the company, liability protection, taxation, and management in order to make the right decision. This article will hopefully make things a little clearer when it comes to types of business organizations.
Types of Business Organizations
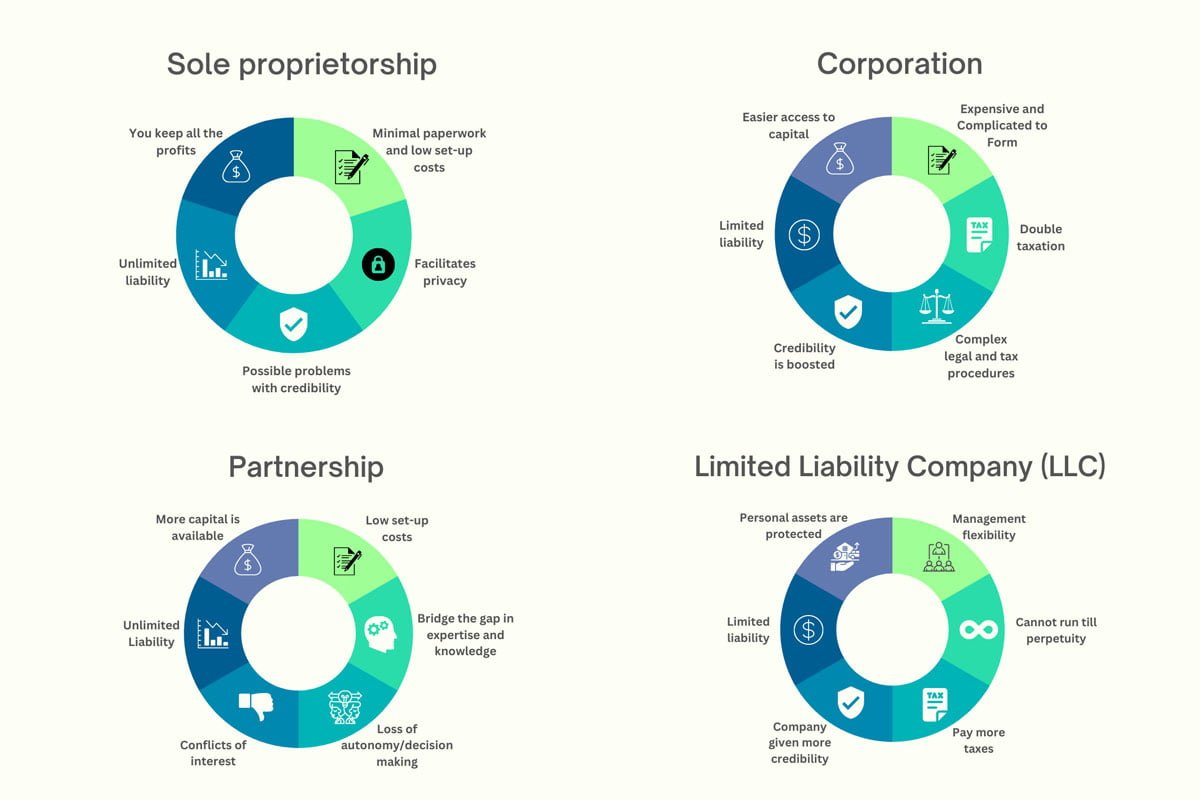
Sole proprietorship
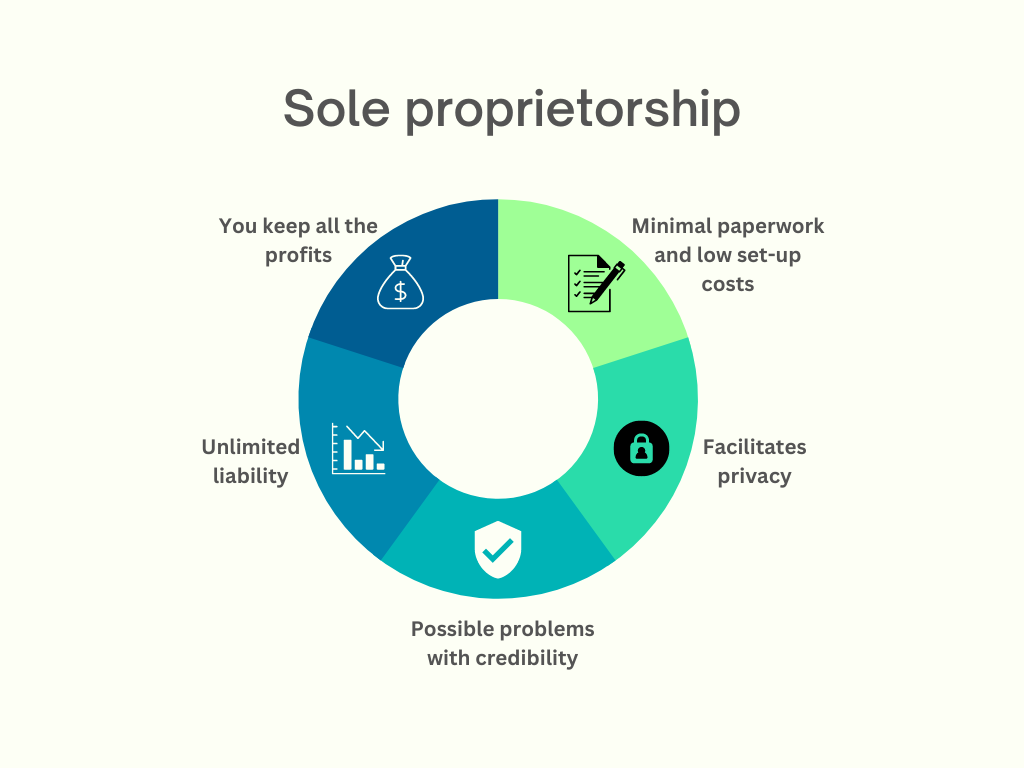
This is probably the simplest and most typical type of company organization on the market today. It relies on having one lone proprietor who oversees every facet of the company. This person has total authority over the business’s operations as its sole owner, plus they can keep all profits. One of the main benefits of a sole proprietorship is minimal paperwork and legal requirements, which makes such businesses simple to start up. It is also the most economical structure for small companies, which is why it’s often chosen by entrepreneurs, independent contractors, consultants, and freelancers.
However, the biggest drawback of this system is the fact that any debts or legal proceedings brought against the company are the owner’s personal responsibility. It’s possible for creditors to pursue the owner’s personal assets, (savings, investments, or properties) if the company is unable to pay its obligations.
Corporation
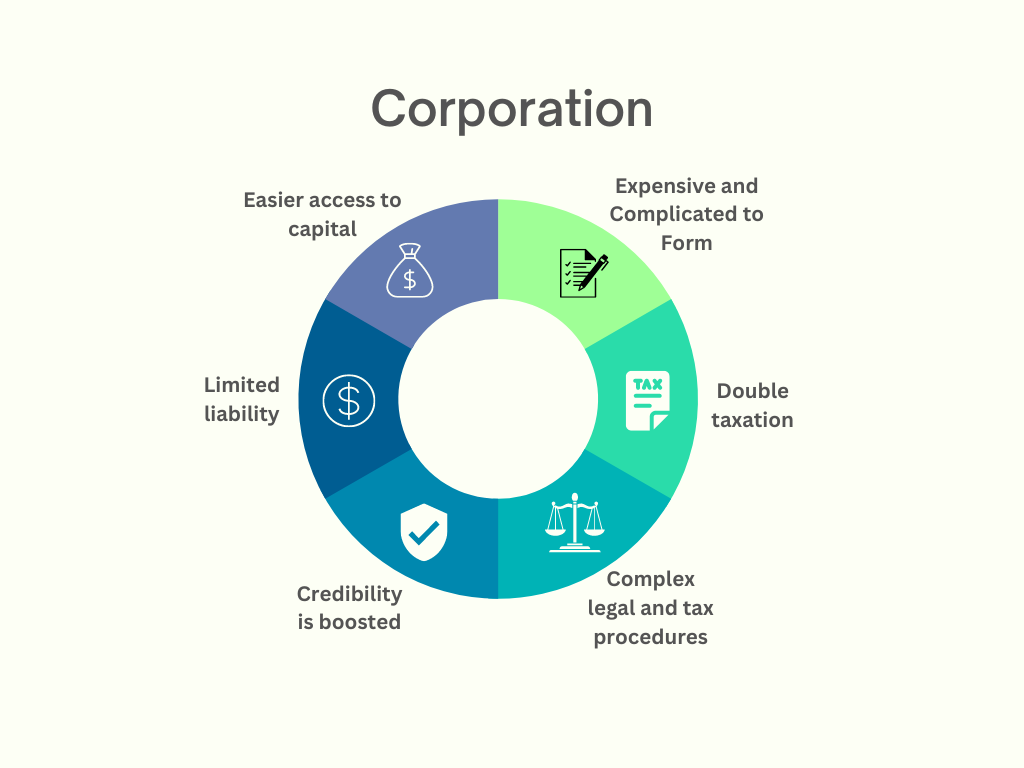
This is a legal entity that “lives” separately from the owner or owners. The biggest advantage of such a system is the limited liability, so shareholders don’t need to fear being personally liable for debts or legal problems. By selling stocks to investors, it’s possible to raise capital, and a corporation can have any number of shareholders. However, it’s crucial for everyone involved to follow a set of complex legal and tax procedures (annual meetings, elections, financial statements, etc.) This is a business model preferred by big businesses and organizations that want to use the public to raise funds.
As stated above, the biggest benefit of a corporation is limited liability protection, but there are also benefits of raising capital through stocks, perpetual existence, ownership separation, management benefits, etc. On the other hand, it’s necessary to follow extensive regulations, pay double taxation, suffer higher legal and accounting fees, enjoy less flexibility, and so on.
Partnership
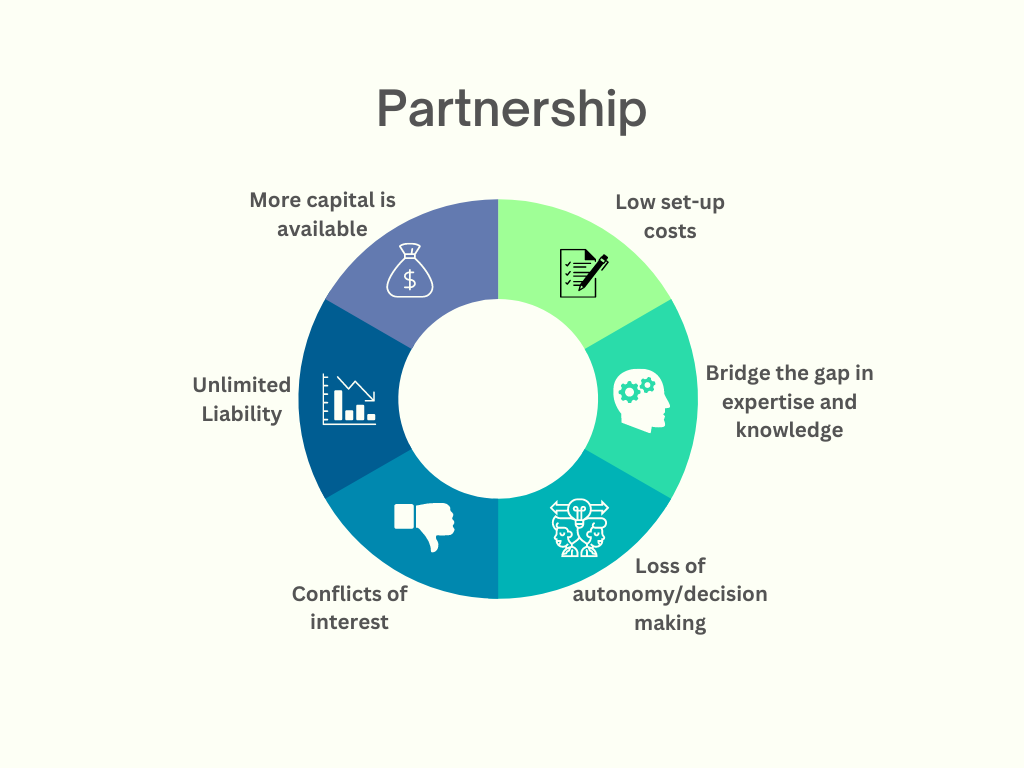
This business model involves two or more owners who share their ownership and management obligations. Partnerships can be general and limited. With a general partnership, all partners are equal in sharing liability and profits while also being able to act for the good of the business and handle responsibilities for each other’s actions. General partners can expect unlimited liability. On the other hand, there’s a limited partnership that includes partners who invest yet have limited liability. Overall, partnerships are a popular choice for small businesses, mainly in the service industry—law firms, accounting, and the medical field. A great example to look at partnerships is the healthcare industry.
There are websites that establish partnerships with medical practices in order to gather them all in one place. On such websites, you can find all the medical specialities you need, including gynaecology, primary care, medical practices, and dermatology specialities, among others.
If there’s a good legal agreement in place, partnerships can work smoothly and be easy to maintain.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
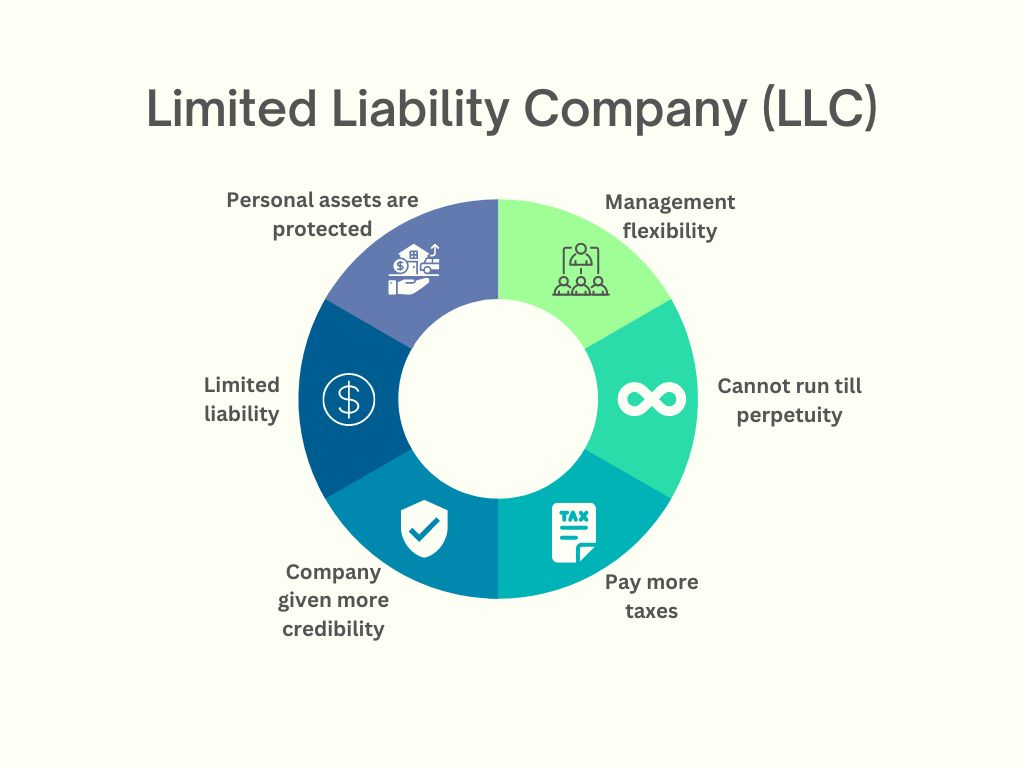
This is a hybrid company structure that combines the advantages of a corporation and a sole proprietorship. In this system, the owners are shielded from personal liability while still being able to declare company earnings and losses on their individual tax returns. LLCs can have one or more members, and each person has the option of running the company themselves or hiring external managers. LLCs provide their users with decent financial benefits, but flexible management structures are what attract most business owners.
Small companies, independent contractors, and real estate investors all favour this system, due to management benefits. LLCs have a number of advantages—pass-through taxation, minimal regulatory requirements, asset security, and flexible management structures. However, LLCs need constant legal and monetary upkeep, such as yearly fees and reports, running contracts, and state filings. An LLC must be dissolved upon the death or bankruptcy of any member It can’t last forever as a business.
Choosing the ideal business organization is a crucial decision that affects the development and success of your business. It is important to take into account factors like liability protection, taxation, management flexibility, and legal requirements because each type of business organization has specific advantages and disadvantages. In order to ensure compliance with state and federal laws and regulations, it is crucial to confer with legal and financial experts regardless of the type of business organization. With these tips in mind, you will be able to select the correct type of business organization from various types of business organizations and will set you up with all the preparation you need to accomplish business objectives and long-term success.