Hello, Guys, we have heard the term “Gear” many times when we talk about vehicles, transmissions, clocks and any mechanical device. Today I am going to try to explain How to Calculate Gear Ratios.
What are the Gears?
In order to understand the gear ratio or calculate it, you need to understand what is gears. It is a wheel with a tooth that is used in mechanical devices. When two gears with teeth are used together to alter the speed or direction of a mechanism it is called a gear set. And when there are multiple gear sets it is called a gear train.
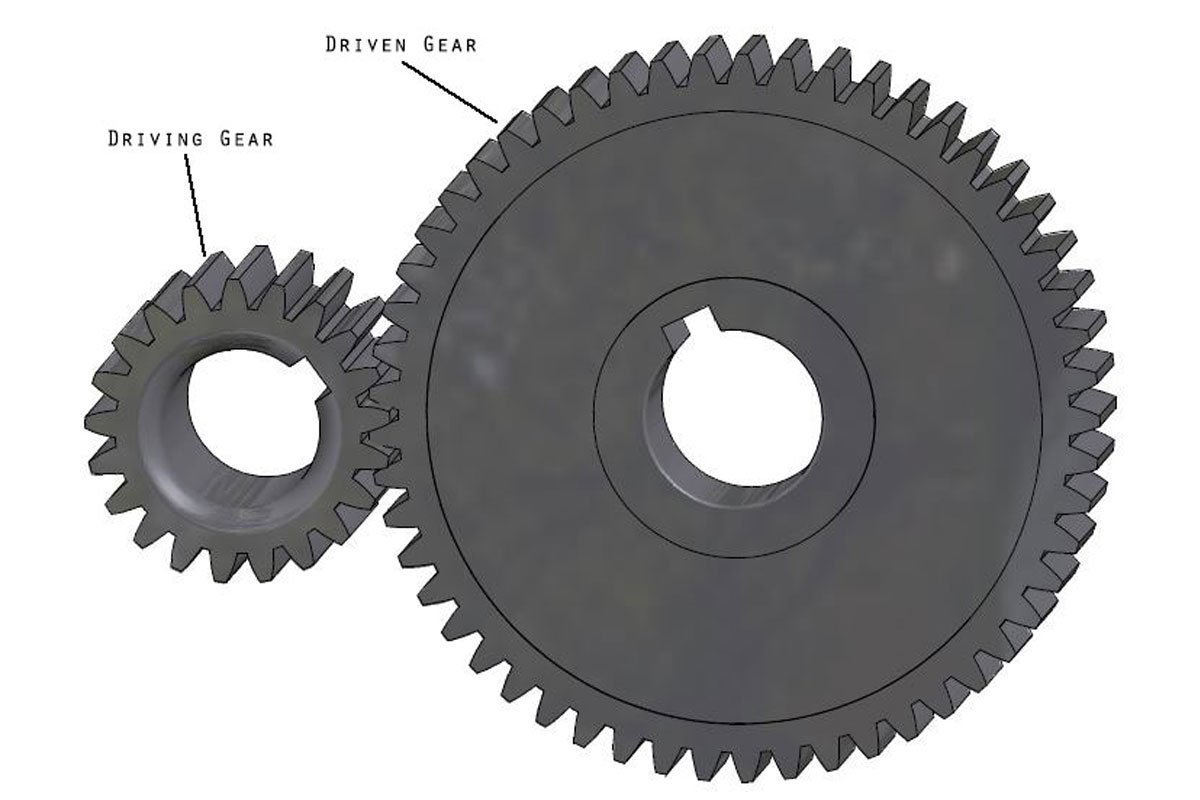
Gears work in pairs. There are two gears a driving gear and a driven gear. A motor rotates the Driving gear and the driving gear rotates the driven gear. A gear ratio is determined by using these two gears.
Gear ratios
The ratio is the number of teeth on the driven gear (ring gear) divided by the number of teeth on the driving gear (pinion gear). For eg, if the driven gear has 36 teeth and the driving gear has 12 teeth, the gear ratio will be 3:1. This also means that for every one driven gear, the driving gear will turn 3 times.
Gear Ratio = Output Gear (Driven Gear) / Input Gear (Driving Gear)
If we reverse this that means we use the 12 teeth gear as the driven gear and the 36 teeth gear as the driving gear. The gear ratio will be 1:3.
Compound Gear Ratio/ Gear Train
If we have compound gear like this with the same number of teeth on driven and driving gear:
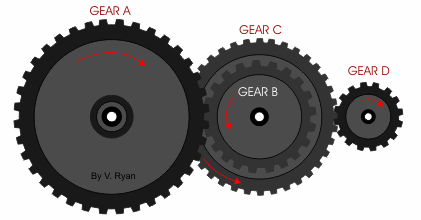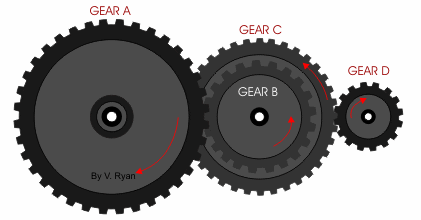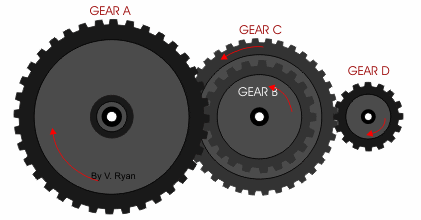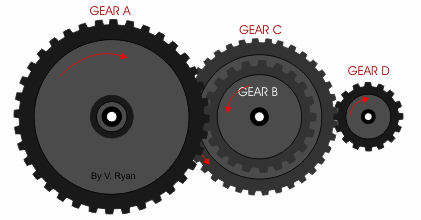
The gear ratio would be 9:1 and vice versa if we reverse the input and output gear. This means the output gear (Gear A) is only moving at 1/9 of the speed of the input gear (Gear D).
The easiest way to calculate the gear ratio of this compound gear train is to consider each gear set individually, starting from the input and moving to the output. Then use the same formula as the single gear set by dividing the number of teeth of the driven gear by the number of teeth on the driving gear.
You can calculate the rpm of the driven gear by dividing the driving gear RPM and the gear ratio. For example, 500 rpm/3 equals 166 rpm. You can also calculate the total gear ratio by multiplying the gear ratios of all the individual gear stages.
Gear Ratios and Torque
The torque is dependent on the size of the driven gear, the larger the driven gear the Larger the torque and the smaller the driven gear Smaller the torque. Suppose you have 48 teeth-driven gears and 14 driving gears your gear ratio would be 3.5:1.
To calculate torque the formula is Torque = Force x Radius, so to calculate the torque of the driven gear to the driving gear use the formula below
Gear Ratio = Driven / Driving = 48 / 14
Force × Radius (Driven gear torque) = 3.5 gear ratio × (Force × Radius (Driving gear torque))
Why Gear Ratio Matters
One of the main benefits of a gearbox is that it allows you to adjust the speed and torque of a motor. A wide selection of available ratios allows for more opportunities to select an accurate speed reduction or torque for a specific application.
Courtesy: Engineering Explained